
Commercial Office Electrical Fit-Out: Guide to Key Cables
 Author : orionelectricalandlightingdesignadmin
Author : orionelectricalandlightingdesignadmin
We are moving towards a digital era. It is evident that technology has a high-level growth and involvement in our lives. In other words one can also say it is the forefront for everything we do on a daily basis. Therefore it is important to know more about office electrical fit-out, as you might never know when you want to start up your work in your own space.
Technology has become the heart of our new digital world and workplaces, but behind that technology the heart of it is the veins or as we call them cables which helps the technology to operate at its best. Therefore, it’s important to understand that we should not neglect technology, and the need to maintain and have a good sound structure to run operations smoothly.
Data Cabling
Data cabling is very important part of that structure as it lays down a foundation for activation and maintenance for it making it a vital part of the operations
Data cabling is known as the longest-lived component of networks. All things above the cable layer from small things like switches to whole workstation undergo various upgrades from time to time before the cabling is refurbished.
It is clear that there has been a shift in the capabilities and need for traffic requirements for various networks and so has the data cabling. Different equipment are joint and integrated on the company’s networks, from printers, computers and workstations to servers and also the main security upgrade of CCTV Cameras and all other operating systems that one needs to work with. Therefore, Cabling is needed by all who are working either in a small quiet office or an industrial platform which has resulted in usage of different cabling even within the same network.
Let’s understand how these data cables are used, how they have developed and what are the specific uses of different cables for you to make the right purchasing decision.
We all have seen so many different types of cables at some point in our lives, either when our homes were being renovated or a building was being constructed in our neighbourhood. But offices and commercial spaces take it up to the next level by using a very high percentage of cables. A whole cable system is laid down for an entire building to run on the same network.
Therefore, even if there are dozens of different types of cables, they all fall under the following three classes of cables:- Coaxial Cable – also known as ‘coax’ uses copper as transmission medium.
- Twisted-Pair Cable – has a different structure but also uses copper as transmission medium.
- Fiber Optic Cable – used optic fibre to carry signals in the form of light.
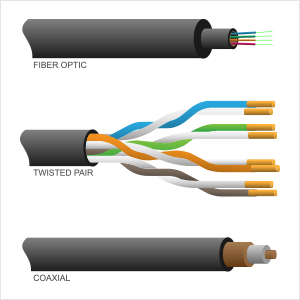 Source: VectorStock
Source: VectorStock
The major factor in the most to cables is its material and build. Both of these factors determine how much the cable will cost, the process of installation and verification and other operations. But they also factor in how they behave.
However, the main factors determining are:- Bandwidth and Latency of your network – how much information can be transmitted in a unit of time (megabytes or gigabytes per second) and the length of time for one unit of information to travel over the cable.
- Distance over which signals of a particular speed can be carried.
- Installation requirements – depending on the material and build of the cable, different connectors are used, also installing the cables requires specific precautions (like protecting cable from elements) or special operations.
Twisted Pair Cable as the name suggests “the network cable” it is the common fabric of user-facing office network and is hence installed mostly on all office floors. It is made of multiple pairs of insulated wires being twisted around each other. In these twisted pairs one of the wires carries the signals and the other is used for ground reference – means one carries the voltage to be interpreted as a data signal wile the other is used by devices at two ends of the cable to make sure what 0 volt means.
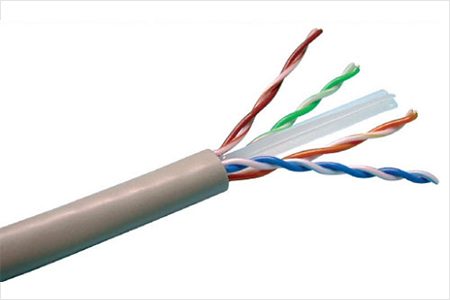 Source: Wire and Cable Tips
Source: Wire and Cable Tips
The cables are twisted together to help reduce the noise from outside sources. While some might do them, but there are some cables which are less susceptible to outside noises. Though they are the most cost-effective out of the three but they have their own disadvantages that they have lower bandwidth and high attenuation.
There are different types of twisted pair cables because of which choosing the correct one is not as simple.
Unshielded Twisted Pair:- It means that they do not depend on physical shielding to bock interference or outside noise.
- It is commonly used for both residential and offices use and is used more than shielded twisted pair.
- There are different UTP categories which as you move up the scale increase their bandwidth.
- CAT1 = up to 1Mbps || CAT2 = up to 4 Mbps || CAT5e = up to 1 Gbps
- It is covered with a foil jacket to block any external interference.
- Is mostly used by high-end applications and by exterior cabling which might be exposed to the environment.
These are high frequency transmission cables which are made of a single copper core. It is rarely seen in computer data networks these days, but it is still used in many TV and radio devices because it has high bandwidth which makes it more accessible for video applications.
 Source: RF Shop
Source: RF Shop
The single copper core has an insulating layer, and another conductive surface serves as a ground reference. Data is transferred electrically over the inner conductor and has high transmission capacity, 80X more than twisted pair cables.
The coaxial cables also have high anti-jamming capacity and can also black signals from outside interference. They have a higher cost as compared to twisted pair cables but also fall under economical category as compared to fibre cables.
These are the latest form of transmission cable. They contain optical fibers which transmit data via light instead of transferring data over copper wires. Every optical fibre is individually coated with plastic layers and stored in a protective tube, which makes it extremely resistant to blocking the external interference.
Therefore, the results are very reliable and it has a super fast connection which has 26000X more capacity then twisted-pair cables. But they have a much higher cost as compared to other cables.
 Source: Indiamart
Source: Indiamart
There are two types of Fiber-optic cables:
Singlemode- It has a small core which allows only one mode of light to pass through at a time. Therefore the number of light reflections decrease when they pass through the core.
- The results lead in low attenuation resulting in data to travel further and faster.
- Commonly used in telecom, universities and CATV networks.
- It is opposite to single mode and has a larger core which allows multiple modes of light to pass through at a time. The number of light reflection also increase as they travel through the core. Allowing more data to pass through.
- Due to high data dispersion, multimodes cables have lower bandwidth, higher attenuation and signal quality reduces the further it travels.
- Mostly used for communication for short distances like security systems, LAN and general fiber networks.
In conclusion each cable has it own functions and uses. It depends which device and your need for a specific office electrical fit-out. If you are renovating your home or planning to shift your business to some office which you want to build from scratch.
At Orion, we specialise in conducting office electrical fit-out. Contact us and we will help you understand which cables will be the most suitable for your needs and will also give you a better idea of a cost at an early planning stage.
